Guided Media
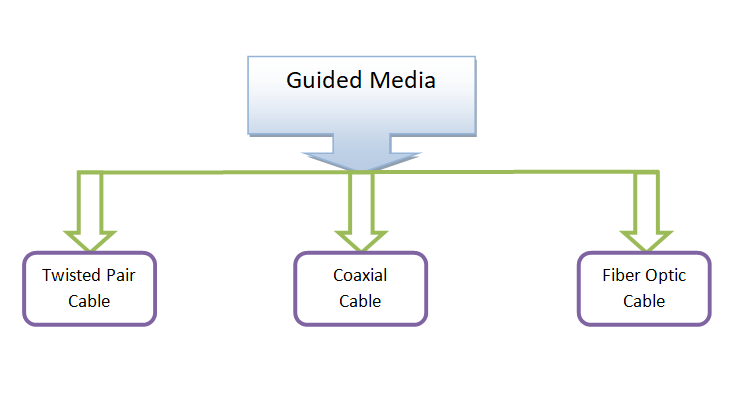
Guided Media in computer networking refers to the physical means through which data signals are transmitted. It is often known as "Wired" or "Bounded" transmission media and is distinguished by its high-speed data transfer and security features. There are three primary types of guided media:
1. Twisted Pair Cables:
Twisted pair cables consist of two insulated wires twisted together, minimizing susceptibility to external electromagnetic interference. They are favored for their simplicity of installation, lightweight design, and cost-effectiveness. Twisted pair cables are commonly employed in telephone lines and local area networks (LANs). However, they have limitations in terms of security, durability, and bandwidth.
2. Coaxial Cables:
Coaxial cables consist of a central conductor within an insulating cover, shielded by metal foil, and an outer plastic covering. They are engineered for high-speed data transmission and excel in noise reduction when compared to twisted pair cables. Coaxial cables serve for both digital and analog transmission, but they tend to be more expensive and are vulnerable to single-point failures within the network.
3. Fiber-Optic Cables:
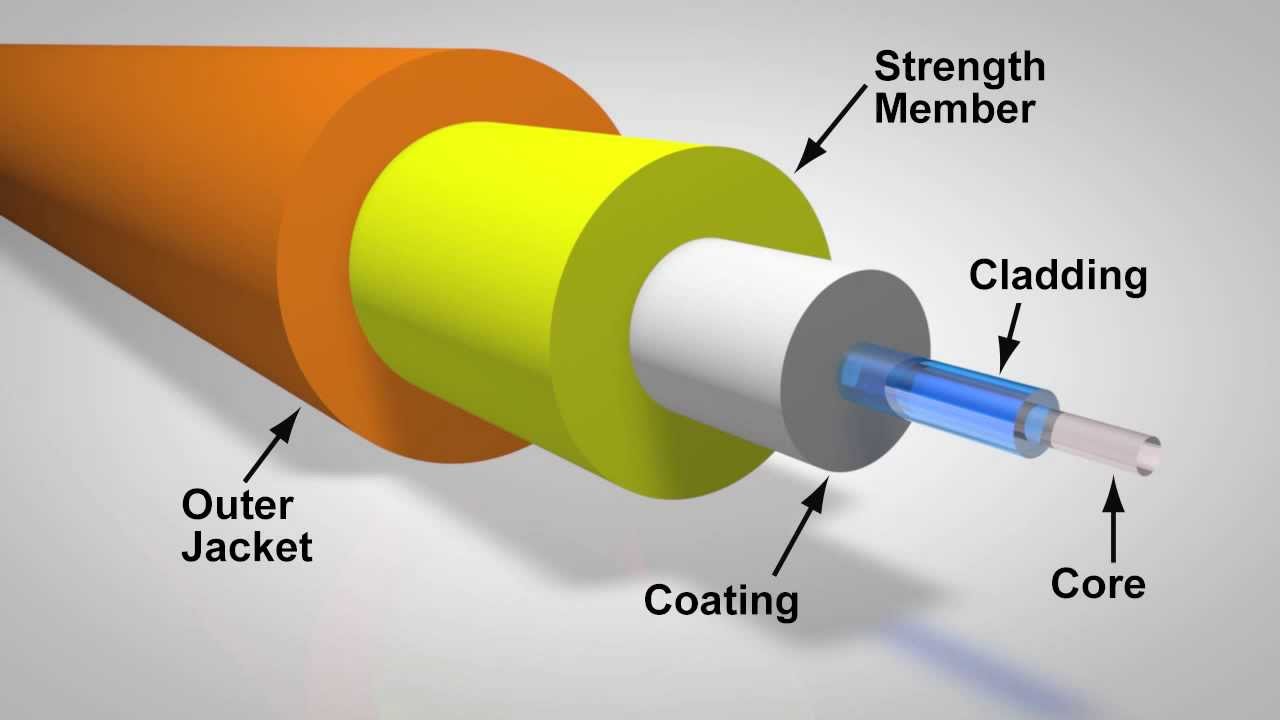
Fiber-optic cables, constructed from glass, rely on light reflection for data transmission. They are renowned for their high bandwidth, rapid data transfer rates, and long-distance capabilities. Fiber-optic cables are more reliable and durable compared to copper cables, as they are less prone to temperature and electromagnetic interference. Their usage is growing for high-speed, long-range data communication.
In essence, guided media provides various options for
transmitting data within computer networks, each offering unique advantages and
limitations. The selection of the medium hinges on factors such as cost
considerations, bandwidth requirements, and the desired level of security and
reliability.
Unguided Media
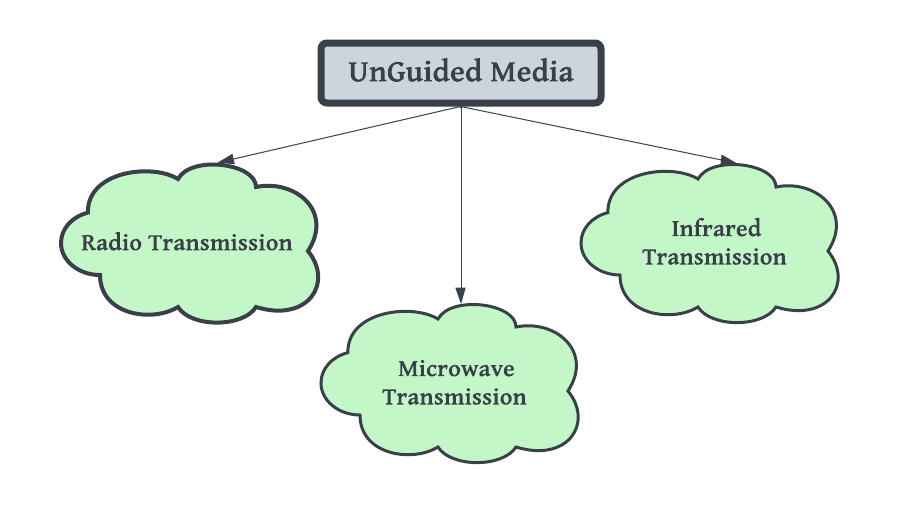
Unguided media, also known as wireless transmission media, does not rely on physical mediums like cables or wires to transfer data from a source to a destination. Instead, it utilizes air as a transmission medium, primarily through the use of antennas to send and receive electromagnetic waves. This approach is essential in scenarios where laying cables is impractical, such as in remote or hilly areas. There are three main types of unguided media:
1. Microwave Transmission:
Microwave transmission operates in the frequency range of 1-300GHz and comes in two varieties – terrestrial and satellite. Terrestrial microwave requires a direct line of sight between sender and receiver, supporting bandwidth from 1 to 10 Mbps, but is sensitive to signal attenuation and adverse weather conditions. Satellite microwave transmission can cover long distances with consistent implementation costs, although installation is complex and costly.
2. Radio Transmission:
Radio waves cover a broad frequency range from 3KHz to 1GHz and are ideal for Wide Area Networks (WANs) like mobile networks. They offer good penetration capabilities but are susceptible to interference from signals of the same frequency, limiting their isolation within buildings.
3. Infrared Transmission:
Infrared waves have the highest frequencies, ranging from 300GHz to 400 THz. They provide high-speed, high-frequency, and secure communication but are suitable only for short-distance communication and cannot penetrate walls, making them ideal for isolated room-to-room communication.
In summary, unguided media plays a vital role in wireless
communication, especially when the deployment of physical cables is challenging
or impossible, offering various options for different communication needs and
distances.